In the case of the off-grid solar system, the solar power system is not connected to the local power grid, instead the system is equipped with its own solar storage system like a battery in order to store excessive electricity produced by the solar panels and store it for later use. The off grid solar power system consists of solar panels, battery, charge controller, grid box, inverter, mounting structure and balance of systems. Off-grid solar systems are ideally used by commercial setups or mid to large sized houses.
The off grid solar system is self-sustaining as it is equipped with a storage facility. It can provide electricity in areas where the power grid is not available or accessible. The off-grid solar system gives you power facility in places where the power grid cannot reach or costs too much to reach. Using the off-grid solar system you have an independent source to fulfill your power requirements. rural areas which are prone to power outages would benefit the most by using off-grid solar systems. This way they can sustain themselves without having to depend upon an unreliable power grid supply.
There are several types of off-grid solar systems you can choose from on the basis of your needs and the investment to plan on doing in solar energy systems. When we talk about the types of off-grid solar power systems, the variations are largely based upon the solar electric panels and electricity that they store in the battery banks.
Before we visit the types of off-grid solar power systems, let us take a quick look at the different components needed for the off-grid solar power system.
The components of Off-grid solar systems:
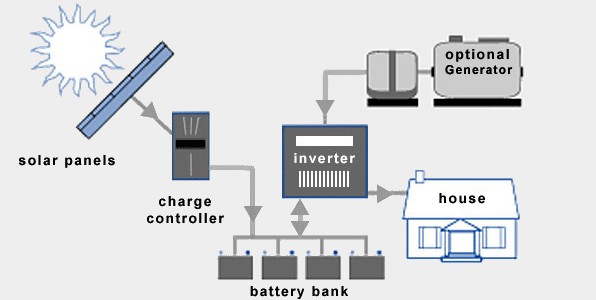
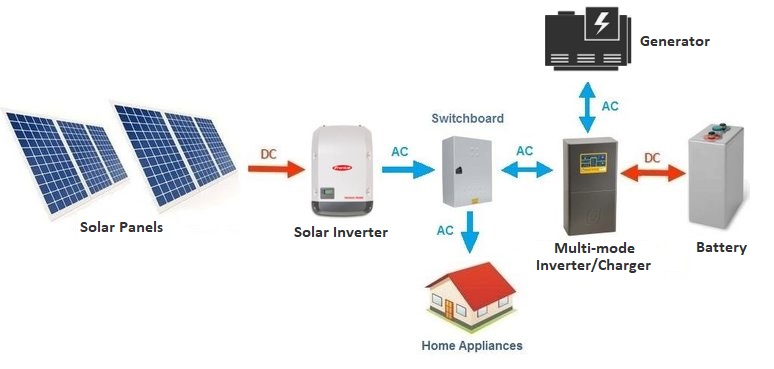
There are a number of components that go into the off-grid solar systems, but for most DC- coupled off grid systems consist of majorly five components.
- Battery Inverter/charger or Multi-mode hybrid inverter
- Solar inverter (AC) or MPPT Solar charge controllers (DC)
- Battery bank
- Solar panels
- Generator (Optional)
In order to go off-grid with a solar power system, you need to install a few additional pieces of equipment. You would need a specific type of off-grid solar system you would require deep cycle batteries as well as backup energy supplies in order to have your own energy source:
Battery for Off-grid solar power system:

When the production of electricity exceeds your consumption, the extra electricity produced needs to be stored, this would need a battery bank. The battery bank will enable you to store the excessive electricity during peak production hours, and utilize it later when the production is low and the consumption is high.
When talking about solar battery storage, you have a number of options available. Majorly there are two main battery chemistries to choose from: lead acid battery and lithium battery. These are further divided on the basis of the way the battery is constructed. In case of the lead acid battery, the two major options available are flooded lead acid batteries and sealed AGM batteries.
In the case of the lithium batteries, the chemical makeup is Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4). They are very different from the Lead acid batteries in terms of size, weight as well as how they charge and discharge. The chemical used in the lithium battery is very safe to use and can be stored without the need for ventilation.
In addition to the battery bank, you also need a backup generator to complete your off-grid solar system. During the times when the solar energy is low because of the weather conditions, even your solar battery wouldn’t last for too long, in this case you would require a backup generator that can fulfill your power needs as well as charge the batteries for you to use the power.
The battery used in case of off-grid solar power systems needs to be larger than that used in case of grid-tied systems. This is because in case of the off-grid solar system, the battery acts as the sole power backup system. While in the grid-tied solar system, you still have the grid power as a source of backup.
Charge controller in Off-grid Solar system:

The charge controller is used to manage the flow of energy from the pv panels to the solar battery. When there is excessive electricity produced, the charge controller directs the electricity to the battery. In addition, the charge controller also ensures that the batteries are not overcharged. This helps maintain the longevity of the battery. There are two main types of charge controllers, one is Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) and Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
A PWM charge controller employs pulse modulation to control the rate at which the energy produced by the solar panels is sent to the batteries for storage. The PWM charger does not allow for much control on managing the power coming from the solar panels. In essence the PWM charge controller merely dumps the power into the batteries, thus they offer limited input when compared with the MPPT controller.
The MPPT charge controllers have an ability to track the maximum point of power that is coming from the solar panels and being delivered to the batteries. Thus they are more efficient. It is able to convert higher voltage / lower current input into lower voltage / higher current output for the same amount of solar power. All of this makes the MPPT charge controller a more efficient and accurate option.
Battery Inverter for off-grid solar system:

In almost all off-grid solar systems, the inverter is battery based inverter. The inverter is used to convert DC power, stored inside the battery bank, to AC power that can be used in electrical appliances. The battery inverter used in off-grid solar systems come in different sizes in order to accommodate the off-grid loads required. It is important to ensure that the inverter can handle all loads running side by side in the system. To determine the maximum amount of loads the inverter should be able to handle, you need to add together all the system loads present in the off-grid solar systems. The inverter also needs to be able to match ‘voltage-wise’ with the system that it is used with. Thus choosing the right inverter for an off-grid solar system is a very important decision to make.
Advantages of Off-grid solar system

One of the biggest advantages of solar as an energy source is its scalability and modularity, which is the degree to which a system’s components may be separated and recombined for flexibility and variety in use.
It works at all levels, from small devices such as solar phone chargers, all the way up to a system that can power a factory.
Here are some of the most common applications of off-grid solar:
- Providing a charge to a portable phone or tablet charger
- Powering the appliances in an RV
- Generating electricity for small cabins
- Powering small energy-efficient homes
- It’s worth noting where off-grid solar systems do NOT make sense: where there is easy access to the utility power. This covers situations where one is looking to power a home in a home in a city, suburb or town.
If that’s you, you can save much more by opting for a grid-tied or hybrid solar panel system — or even just sticking solely to grid power — depending on the economics of solar in your area.
Disadvantages of off-grid solar system

While off-grid solar systems afford a number of advantages, they also have a few disadvantages that are worth taking a look at. More expensive than grid-tied solar systems: since the off-grid system requires additional equipment to be installed, it becomes more expensive to install than the grid-tied solar system. More tedious to install: because the off-grid solar system needs a number of different equipment, it becomes more tedious to install. It is more time consuming and takes a lot of work.
Limited power backup: the off grid power system needs a bigger battery bank than does an on-grid solar system. Even then, the battery bank cannot sustain the power usage. At best, a battery can sustain the house for a few hours. Thus, the off-grid system also needs a backup generator. Thus the off-grid solar system has a limited capacity to generate power.
Types of off-grid solar system:
There are different types of off-grid solar systems to choose from when you choose solar power for off-grid living. The following use AC or DC system power in various configurations:
Off-Grid DC Solar Power Systems
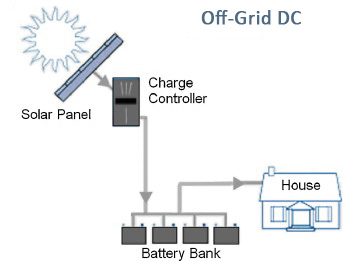
DC (direct current) off-grid solar power systems are most often used in off-grid living to power DC appliances in RV’s, boats, and cabins, as well as farm/ranch appliances like cattle gates and rural telecommunications systems when utility power is not accessible.
DC solar power is less expensive than AC solar power because an inverter is not required to convert the electricity produced by solar panels and stored in batteries from DC to AC. But DC solar power does NOT power standard AC appliances.
DC only systems are generally small systems powering lighting and low consumption appliances such as monitoring equipment. The solar panels or wind generator charge the battery and the battery supplies power to the loads. All loads are run at the battery voltage, typically 12V or 24V DC. Charge controllers limit the charging when the batteries are full. Since there is no backup generator, it must be sized to meet the load for worst case conditions.
Off-Grid AC Solar Power Systems
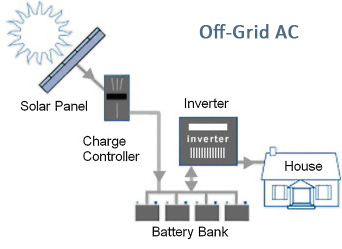
Off-grid solar power also stores DC electricity in batteries. The addition of an inverter allows this system to convert DC electrical current coming from the batteries into AC, or alternating current. AC is the standard form of electricity for anything that “plugs in” to utility power and is the appropriate current for common household appliances.
While AC off-grid solar power systems are more expensive solar power options for off-grid living because of the cost of the inverter, you can provide power to a greater variety of appliances.
With an AC only system, all of the loads are run on AC using an inverter to convert power stored in the battery bank to 230V AC. Grid connected homes all run off 230V AC and thus the wiring for an off-grid home with an AC only system will be the same as the wiring for a grid connected home, using low cost cable and components. Once again, note that without a backup generator, the system must be sized for worst case conditions.
Off-Grid Solar Power for Remote Telecommunications

Small off-grid DC solar power systems can power telecommunications, security, and lighting systems in locations for off-grid living, far away from power lines. Visit our remote industrial power page to learn about self-contained solar kits for a variety of industrial applications.
Off-grid hybrid systems are another, far less commonly used option that combine off-grid solar with gas or wind generators, but keep in mind that to go this route, your area needs substantial wind speed to justify a turbine.
Want to find out more about using solar power for off-grid living? Explore our off-grid solar packages to see how you can afford to get off the grid with solar.
AC system with wind and solar
The AC system can have two sources of renewable energy:
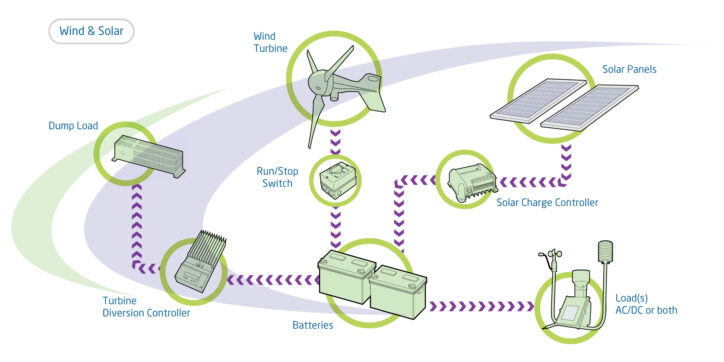
AC system with backup
To avoid sizing for worst case conditions, a backup generator is used. A petrol, LPG, or diesel generating set combined with a battery charger can supply power if the batteries
PV direct systems:
Load is run directly from a solar array, without energy storage (batteries). • Generally used only with motors, like pumps and fans, which can run directly from a DC energy source. Well pumps are the most common load • Loads can only run when energy is available from the production source since there is no energy storage • Very simple systems– minimal equipment needed, such as solar array, direct drive controller, and the load • Loads run at variable speed depending on energy available from source: PV-direct systems do not work at night • Current limited: only the amount of current that is directly produced by the energy source is present. Often means that overcurrent devices are not needed as long as the conductors are sized to handle full current.
Sizing of off-grid system:

Sizing of an off-grid system requires modelling of the expected output from the renewable energy system, and of the load that the system must meet.
The three key variables are as follows:
- kW output of renewable generator(s);
- kWh of battery storage;
- kW output of back-up generator.
- In addition the battery voltage must be compatible with the charger.
Renewable energy generation is by nature intermittent, and the battery storage system and / or generator must be sufficiently large to cover the times when the generation is unable to meet the load. Typically the generator output (kW) is sized to cover peak load, and thus it serves as a full power back-up. The renewable energy system and battery storage can either be sized to reduce the contribution of the back-up generator below a certain minimum (e.g. 10% of annual load), or it can be optimised to minimize the lifetime cost per kWh.
Modelling the Renewable Output
There are established models which can be used to estimate the hourly output of a solar PV or wind generator in a given location. For solar, the model should include shading analysis to establish the impact of any shading. For wind, the model must be very localised, taking into account average wind speed, prevailing wind directions, and seasonal variations.
Note that wind and sun are generally complementary (high winds and low sun in winter) and so, depending on location, it may be advisable to combine both.
Powering down
If the renewable energy system is ‘over-sized’ it will need to be powered down in favourable conditions (wind or sun) as there may be nowhere for the full output to go (e.g. if the battery is already full). There is a balance between how often the system has to power down due to ‘over-sizing’ in favourable conditions and how often the generator has to be used due to ‘under-sizing’ in unfavourable conditions.
Modelling of the loads
Modelling of the loads requires a systematic exercise of listing all of the loads (dc and ac), including running currents and start-up currents.
An ‘hourly profile’ should then be built up for each load, to give an average consumption by hour. Consideration should also be given to the peak load if all key loads are run together.
Grid-Tied Vs. Off-Grid?
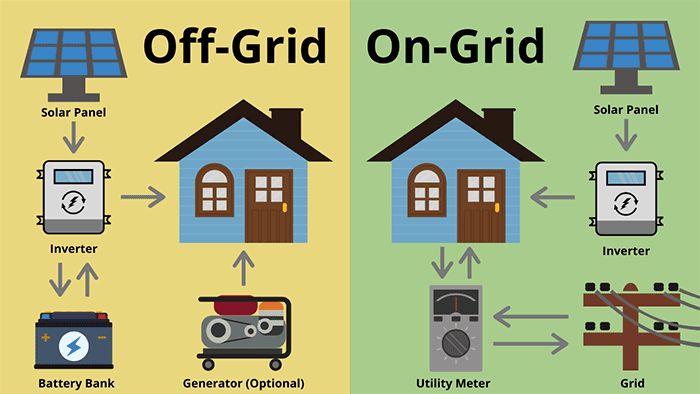
The difference between grid-tied vs. off-grid solar is where you store the energy your panels produce. With grid-tied systems, the energy you generate is sent to the power grid. The utility company then credits you for the power you generate— similar to how you deposit money into a bank for later use.
Without access to the grid, an off-grid system requires a battery bank to provide dedicated energy storage and power to meet your energy requirements throughout the year.
Off-grid systems are typically more expensive than grid-tied systems due to the cost of batteries, system requirements, off-grid solar products, and having the best off-grid inverters to manage power flow. Still, off-grid solar is a cheaper alternative than running power lines all the way out to a remote property.
